What is Low Testosterone (Low-T)?
The medical term for Low-T is called Hypogonadism which is a failure of the gonads or testes in men to function properly. This causes a decrease in the production of testosterone, hence the name Low-T.
What is Testosterone and why is it important?
Testosterone Molecule
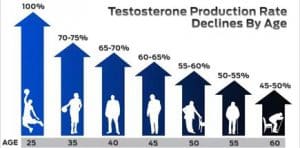
Testosterone is responsible for regulating sex drive (libido), bone mass, fat distribution, muscle mass and strength, and the production of red blood cells and sperm. Unfortunately, as men age their production of Testosterone declines. In general, 1 in 3 men will have a reduction in Testosterone that affect their daily activity and normal routines. The medical condition Hypogonadism (Low Testosterone) is a progressive condition and only gets worse the older men get. The graph below is a great representation of what the production rate is as men age. The decline can be severe over time, but for some men, that decline happens at a much earlier age and requires treatment. In men, symptoms start to appear as early as age thirty and will progress as they age. A large misconception that men have is that this is the natural process of aging and nothing can be done. The reality is that it is not. This hormonal imbalance can be treated and corrected getting them back to their normal life.
Symptoms can include but not limited to:
- Fatigue
- Decreased Libido (interest in sex)
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Weight Gain/Loss
- Loss of Muscle Mass
- Signs of Depression/Anxiety
- Hair Loss
- Mental Fog/ General Loss of Interest
Hypogonadism can be defined as either Primary or Secondary.
Primary means that you do not have enough sex hormones in your body due to a problem in your gonads. Your gonads are still receiving the message to produce hormones from your brain, but they are not able to produce them.
Secondary means the testicles are normal but do not function properly due to a problem with the pituitary or hypothalamus. Several conditions can cause secondary hypogonadism, including but not limited to:
- Kallmann’s syndrome
- Prolactinoma (Pituitary Tumors)
- Sleep Apnea/Insomnia
- Chronic/Autoimmune Disease
- Opioid/Alcohol Abuse
The good news is that even though there isn’t a cure for Low-T there is treatment available. Treatment of Hypogonadism is called Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT). There are several treatment options but two of the most common and effective are:
- Testosterone Cypionate Injections
- Topical Testosterone Cypionate
TRT, however, is not a quick fix and requires a long-term treatment plan. Treatment will normalize Testosterone Levels within a few short weeks though and clients can expect to see positive changes in a short time frame. The treatment is ongoing and if you stop treatment, your body will revert back to previous levels or to what it would be capable of producing at that point in time. Patients can expect:
- Decrease in fatigue
- Increase in libido (sex drive)
- Spontaneous Erections/Morning Erections
- Improved Mental Clarity
- Weight Loss
- Improved Muscle Mass
- Reduced Recovery Time
- Heightened Endurance
Men’s Total Health is committed to diagnosing this highly treatable condition. Every client will receive a personalized approach to his specific hormonal needs. A simple morning blood test is all it takes to diagnose with results in 15 mins. In your first appointment, you will receive the testosterone test along with a thorough and complete consultation. Men’s Total Health is committed to the wellness and health of our patients and to improve their quality of life. We are helping men live longer and happier lives.
